Introduction
A load cell is a highly accurate device used to measure force or weight. They are integral components in various industries due to their precision and reliability. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the fundamental aspects of load cells, including their purpose, applications, working principles, and different types. Additionally, we’ll address common questions and provide insights into related technologies.
What is a Load Cell?
A load cell is a transducer that converts mechanical force into an electrical signal. The signal can be measured and used to determine the weight or force applied to the load cell. Load cells are essential for ensuring accuracy in weight measurement systems.
What is the Purpose of a Load Cell?
The primary purpose of a load cell is to provide precise weight measurements. They are crucial in industries where accuracy is paramount, such as manufacturing, transportation, and healthcare. Load cells ensure that products are weighed correctly, enhancing quality control and operational efficiency.
What are the Applications of a Load Cell?
Load cells are used in various applications, including:
- Weighbridges and Truck Scales: For weighing large vehicles.
- Industrial Scales: For manufacturing and production processes.
- Medical Equipment: Such as patient lifts and scales.
- Automotive Testing: For measuring force in vehicle components.
- Aerospace: For testing and measuring aircraft components.
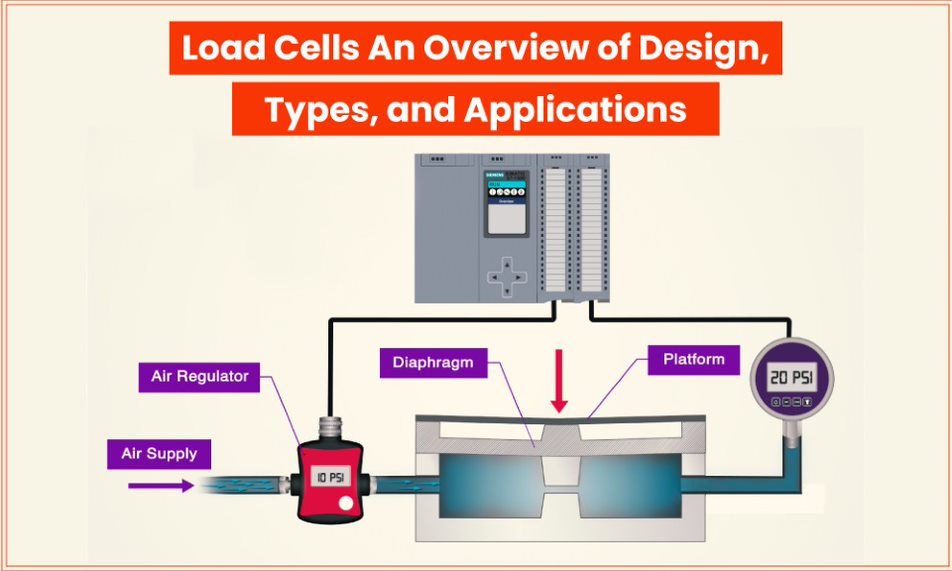
How Do Load Cell Sensors Work?
Load cells operate based on the principle of strain gauges, which deform under load. This deformation changes the electrical resistance, which can be measured and converted into a readable output. The change in resistance is proportional to the force applied, allowing for precise weight measurement.
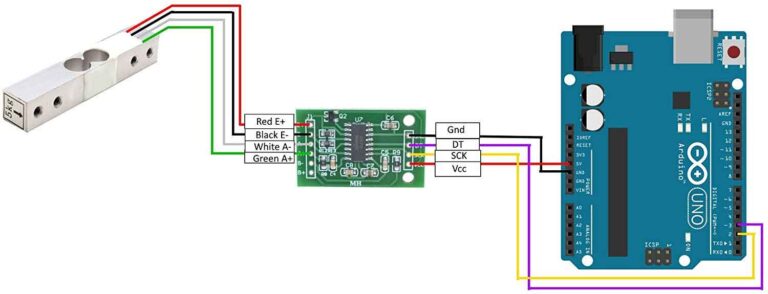
Do Load Cells Need a Power Supply?
Yes, load cells require a power supply to operate. The power supply is necessary to energize the strain gauges within the load cell, enabling them to produce an electrical signal proportional to the load applied.
Does a Load Cell Make You Faster?
This question is a bit misleading. A load cell itself doesn’t make processes faster, but its precise measurements can improve efficiency in production and quality control, indirectly contributing to faster and more accurate operations.
What are the 4 Types of Load Cells?
There are four main types of load cells:
1.Strain Gauge Load Cells: The most common type, known for accuracy and versatility.
2.Hydraulic Load Cells: Use fluid pressure to measure weight.
3.Pneumatic Load Cells: Use air pressure to measure weight.
4.Capacitive Load Cells: Use changes in electrical capacitance to measure force.
What is Another Name for a Load Cell?
A load cell can also be referred to as a force sensor or weight transducer. These terms are often used interchangeably in the industry.
What is the Difference Between a Force Transducer and a Load Cell?
While the terms are often used interchangeably, a force transducer typically refers to a device that measures any type of force (tension, compression, etc.), whereas a load cell specifically measures weight or force in a linear fashion.
What is the Alternative to Load Cells?
Alternatives to load cells include:
- Force Sensing Resistors (FSRs): For lighter loads.
- Piezoelectric Sensors: For dynamic force measurement.
- LVDTs (Linear Variable Differential Transformers): For displacement and position sensing.
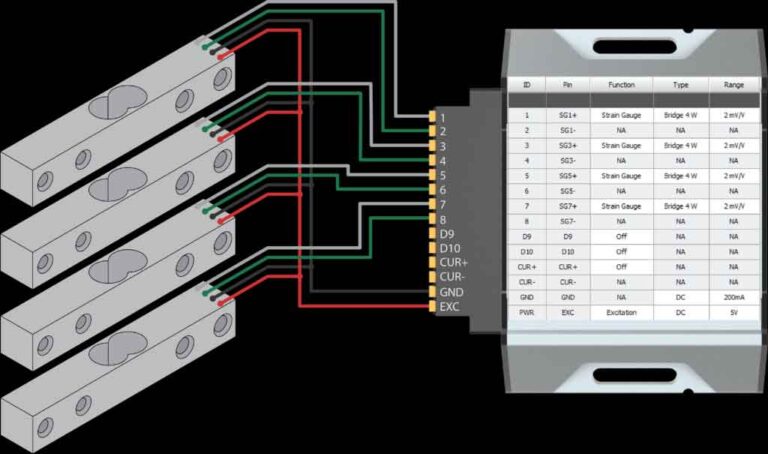
How Many Load Cells Do I Need?
The number of load cells required depends on the application. For example, a standard scale typically uses four load cells, while a more complex system like a weighbridge may require multiple load cells to distribute and measure weight accurately.
Conclusion
Load cells are versatile and essential components in many industries. Understanding their purpose, applications, and types can help you choose the right load cell for your needs. For more information on high-precision load cells, visit Hengli Sensor Co., Ltd.